Introduction to Plastic Credits
The growing concern over plastic waste and its detrimental impact on the environment has led to innovative solutions, among which plastic credits have emerged as a promising mechanism. This article delves into the concept of plastic credits, tracing their origins, operational mechanisms, criticisms, and their potential future.
Understanding Plastic Credits
At its core, a plastic credit represents a quantifiable amount of plastic waste that has been responsibly collected and either recycled or properly disposed of, ensuring it does not pollute the natural environment. This system is akin to carbon credits but specifically targets the pervasive issue of plastic waste.
The primary aim of plastic credits is to provide a financial mechanism that incentivizes the reduction, collection, and recycling of plastic. By allowing organizations and individuals to purchase credits, the system assigns a monetary value to the management of plastic waste, thereby encouraging more sustainable practices. This market-based approach seeks to complement efforts to reduce plastic use at the source while also addressing the plastic that has already entered the waste stream.
History of Plastic Credits
The concept of plastic credits emerged as a response to the increasing challenges companies face in managing post-consumer waste within complex waste management systems. It’s a part of the broader environmental crediting systems, such as carbon credits, aimed at mitigating environmental impacts. Plastic credits represent a transferable unit that corresponds to a specific quantity of plastic waste, aiming to “balance” a company’s plastic footprint by paying for the removal of an equivalent amount of plastic from the environment.
The system was developed partly due to the need for more effective solutions in handling the plastic waste crisis and as a way for companies to take action on their plastic pollution impact. However, this emerging market and its mechanisms, such as the concept of plastic neutrality, are still in the nascent stages, and there’s a consensus among environmental organizations that the development, implementation, and adoption of plastic credits must ensure a transformational impact on both people and nature.
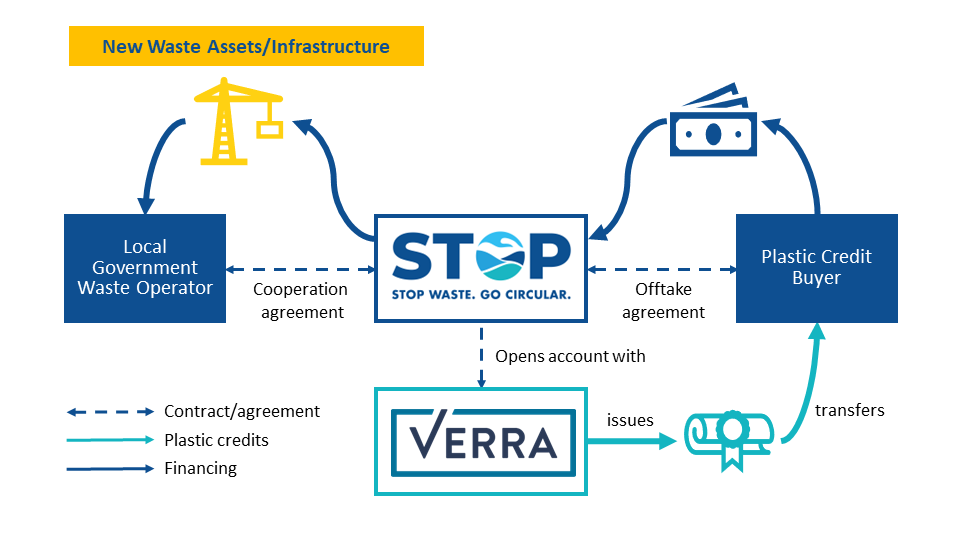
How Plastic Credits Work
The operation of plastic credits is a multifaceted process that combines environmental conservation efforts with market-based mechanisms.
Measurement of Plastic Footprint
The first step involves quantifying an entity’s plastic footprint, which includes assessing the amount of plastic used, discarded, and managed within its operations. This step is crucial for determining the amount of plastic that needs to be offset through the purchase of plastic credits.
Credit Generation
Plastic credits are generated through projects that collect and recycle plastic waste. These projects must adhere to specific standards to ensure that the plastic waste is managed in an environmentally responsible manner. The projects can vary widely, from community-based waste collection initiatives to advanced recycling technologies.
Purchase and Offset
Organizations or individuals can purchase plastic credits to offset their plastic footprint. The purchase of these credits is essentially an investment in plastic waste management and recycling projects. This system allows entities to take responsibility for their plastic waste by funding the removal of an equivalent amount of plastic from the environment.
Verification and Certification
To maintain integrity and trust in the plastic credits system, the generation and retirement of credits are subject to strict verification processes. Independent third-party auditors assess projects to ensure that they deliver the promised environmental benefits. This verification process is crucial for providing transparency and accountability within the system.
Environmental and Social Impact
The funds raised through the sale of plastic credits support various environmental and social initiatives. These can include improving waste management infrastructure, investing in recycling technologies, and empowering communities involved in waste collection and recycling efforts. By channeling funds into these areas, plastic credits can contribute to broader environmental conservation and social development goals.
Regulation and Standardization
While the plastic credits market is still evolving, there is a growing need for standardization and regulation to ensure consistency, credibility, and impact. Establishing clear guidelines and standards will help mitigate risks such as greenwashing and ensure that plastic credit schemes genuinely contribute to reducing plastic pollution.
Complementing Broader Environmental Strategies
It’s important to note that purchasing plastic credits should not be seen as a sole solution to plastic pollution but rather as part of a broader, comprehensive approach to environmental sustainability. Entities are encouraged to prioritize reducing their plastic use and enhancing recycling and waste management practices in conjunction with purchasing plastic credits.
By following these steps, the plastic credits system aims to create a market-driven solution to the plastic pollution crisis, providing a mechanism for entities to mitigate their environmental impact while supporting global waste management and recycling efforts.
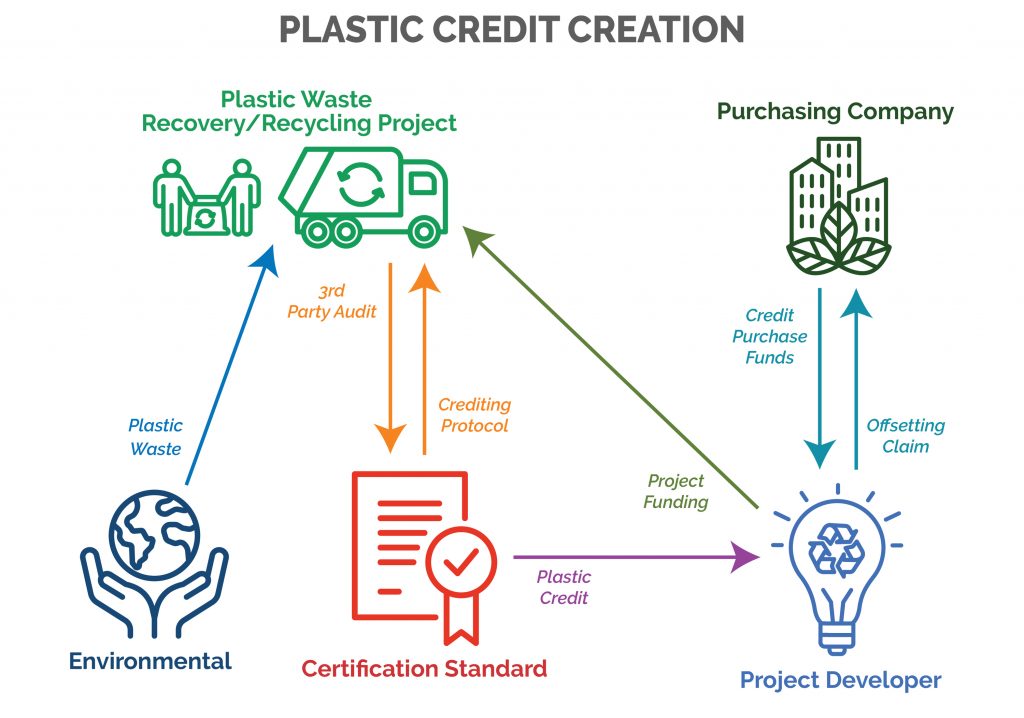
Criticism and Challenges
Despite their potential benefits, plastic credits face criticism and challenges. Some argue that they allow businesses to buy their way out of responsibility for reducing plastic use, rather than implementing more sustainable practices. There are also concerns about the accuracy and transparency of plastic waste reduction and recycling claims, the risk of exacerbating inequalities within the waste management sector, and the potential for credits to distract from the urgent need for systemic changes in plastic production and consumption patterns.
Future of Plastic Credits
The future of plastic credits is contingent on addressing current criticisms and enhancing the system’s integrity and effectiveness. This includes establishing clear standards, improving verification processes, and ensuring that plastic credits are part of a broader strategy that includes significant reductions in plastic use. Innovations in plastic waste management and recycling technologies, along with greater regulatory support and public acceptance, could bolster the role of plastic credits in achieving a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Plastic credits represent a novel approach to tackling the plastic pollution crisis, offering a mechanism for organizations and individuals to take responsibility for their plastic footprint. While they hold promise as part of a multifaceted solution to plastic waste, their effectiveness depends on rigorous standards, transparency, and a commitment to reducing overall plastic usage. As the system evolves, it will be crucial to balance the benefits of plastic credits with the imperative to pursue broader environmental and societal changes in our relationship with plastic.
About GreenUP
Pioneering the Green Transition with Expertise and Innovation. With over 10 million I-RECs issued since 2019, we are Vietnam’s leaders in renewable energy certification. Our comprehensive suite of services, positions us uniquely as a one-stop solution for all your green and ESG needs. Experience unparalleled market access, competitive pricing, and strategic partnerships that drive not only cost savings but also significant value to your sustainability goals.
References
- Green Earth. (n.d.). The Ultimate Guide to Plastic Credits. Retrieved from https://www.green.earth/blog/the-ultimate-guide-to-plastic-credits
- SEA circular Project. (2024, February 2). Plastic Credits: Understanding the Risks and Opportunities in Addressing Plastic Pollution – SEA circular Project. Retrieved from https://www.sea-circular.org/news/a-brief-overview-regional-dialogue-on-plastic-credits-by-sea-circular/
- Simon, E., & Martin, E. (2024, February 2). Putting the Credible in Plastic Crediting. World Wildlife Fund and The Circulate Initiative. Retrieved from https://www.worldwildlife.org/blogs/sustainability-works/posts/putting-the-credible-in-plastic-crediting
- Pekow, C. (2023, November 1). As companies buy ‘plastic credits,’ are they reducing waste or greenwashing? Basel Action Network. Retrieved from https://www.ban.org/news/2023/11/1/as-companies-buy-plastic-credits-are-they-reducing-waste-or-greenwashing
- Verra Views. (n.d.). Five Things You Should Know About Plastic Credits. Retrieved from https://verra.org/verra-views/five-things-you-should-know-about-plastic-credits/
- Stop Ocean Plastics. (n.d.). Our Approach: Plastic Credits. Retrieved from https://www.stopoceanplastics.com/en_gb/our-approach/plastic-credits/
- Sustainable Brands. (n.d.). What Are Plastic Credits? A 4-Minute Explainer. Retrieved from https://sustainablebrands.com/read/defining-the-next-economy/what-are-plastic-credits-a-4-minute-explainer







